Introduction
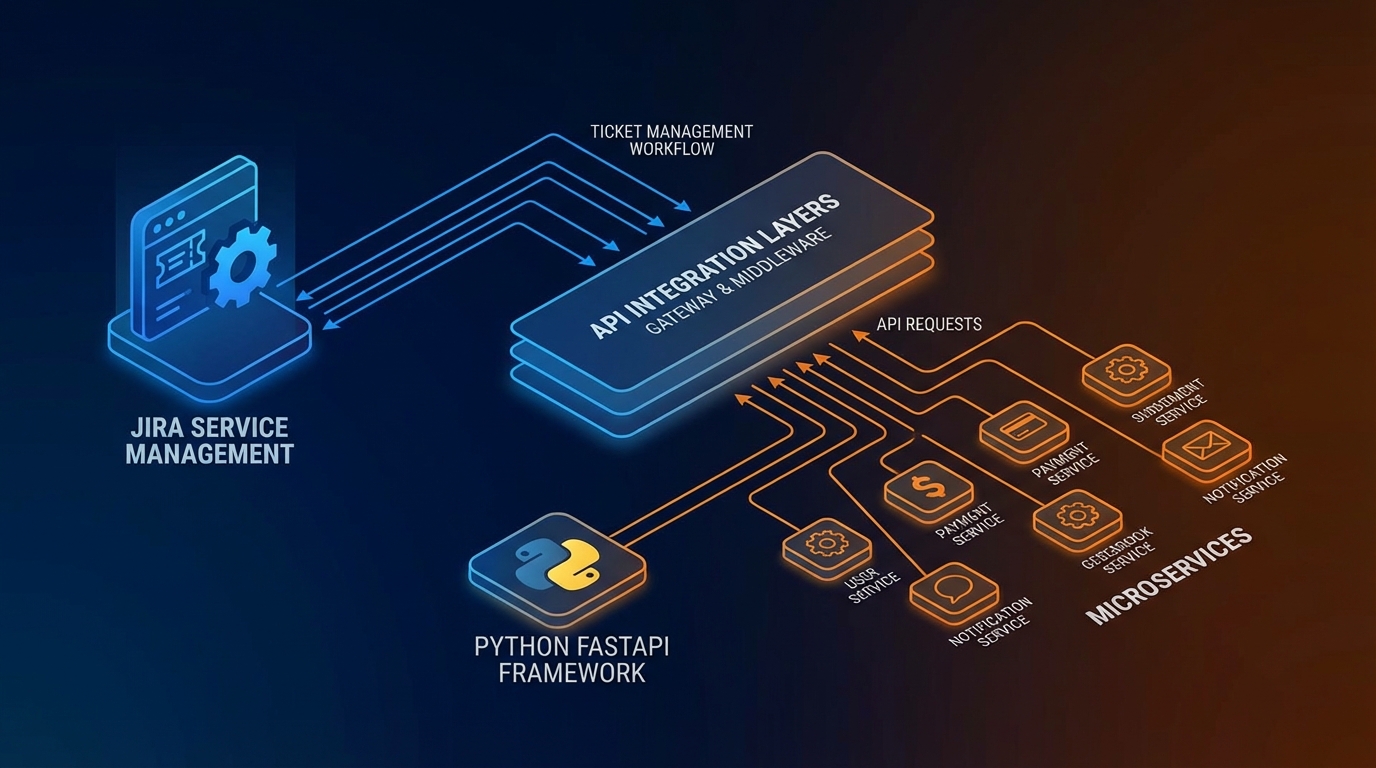
In enterprise environments, bridging the gap between internal applications and support systems is crucial. I needed a way to programmatically create and manage Jira Service Management tickets from various microservices, ensuring that every system alert or user report was properly tracked.
The Solution: A Dedicated Integration Service
I architected a standalone Python microservice designed specifically to handle the complexities of the Jira API, providing a clean, simplified interface for other internal services.
graph LR
subgraph "Internal Microservices"
MS1[Service A]
MS2[Service B]
MS3[Service C]
end
subgraph "Integration Layer"
Integration[Jira Integration Service]
Validation[Config Validator]
Health[Health Checker]
end
subgraph "External"
Jira[Jira Service Management API]
end
MS1 -->|Create Ticket Request| Integration
MS2 -->|Create Ticket Request| Integration
MS3 -->|Create Ticket Request| Integration
Integration -->|Startup Check| Validation
Integration -->|Periodic Check| Health
Integration -->|REST API Calls| Jira
Validation -.->|Verify| Jira
Health -.->|Test Connection| JiraKey Architecture Decisions
1. Configuration Validation as Code
One of the biggest pain points in integrations is misconfiguration. I implemented a strict validation layer using Pydantic. On startup, the service performs a “pre-flight check”:
- Validates all environment variables.
- Tests connectivity to the Jira instance.
- Verifies API token permissions.
If any check fails, the service refuses to start, preventing silent failures in production.
# Simplified validation logic
def validate_startup():
try:
check_env_vars()
verify_jira_connectivity()
check_project_permissions()
logger.info("✅ Jira Integration is healthy")
except ConfigError as e:
logger.critical(f"❌ Startup failed: {e}")
sys.exit(1)2. Resilient Error Handling
The Jira API can be rate-limited or temporarily unavailable. To handle this, I implemented:
- Exponential Backoff: Automatically retrying failed requests with increasing delays.
- Circuit Breaker Pattern: Temporarily disabling the integration if error rates spike, preventing cascading failures.
3. Security First
Credentials are never hardcoded. The service uses a tiered configuration system:
- Environment Variables: For standard deployment.
- Encrypted Secrets: Optional support for encrypted credentials in high-security environments.
- Audit Logging: Every interaction with Jira is logged (without sensitive data) for compliance.
Health Checks & Observability
I treated “observability” as a first-class feature. The service exposes granular health endpoints:
/health/jira/quick: Fast check for load balancers./health/jira: Deep diagnostic check that actually pings the Jira API to verify read/write access.
Conclusion
By wrapping the complex Jira API in a robust, self-validating Python service, I significantly reduced the operational overhead of managing support tickets. The result is a “set it and forget it” system that just works.
Tags